A. Selection Of Materials
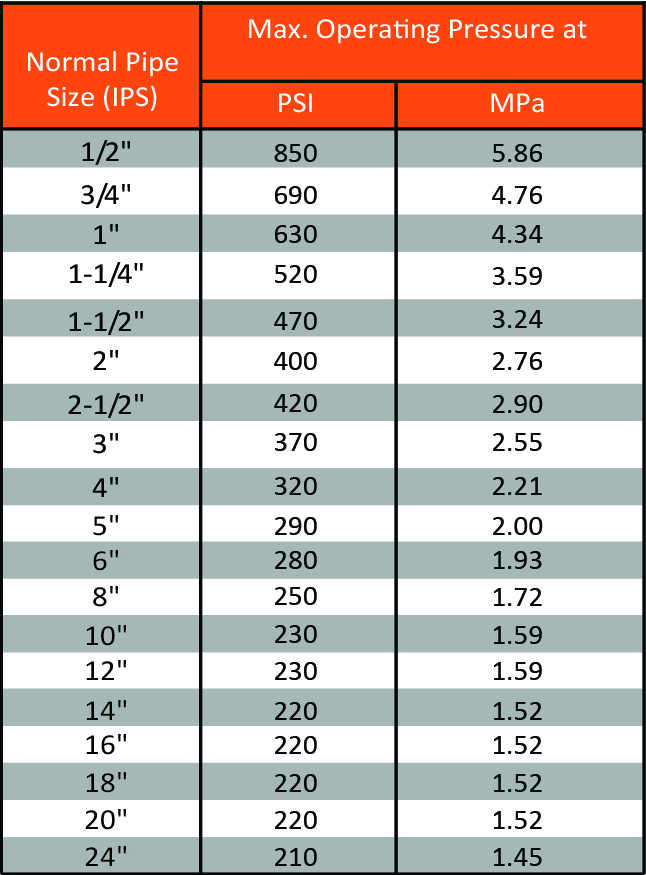
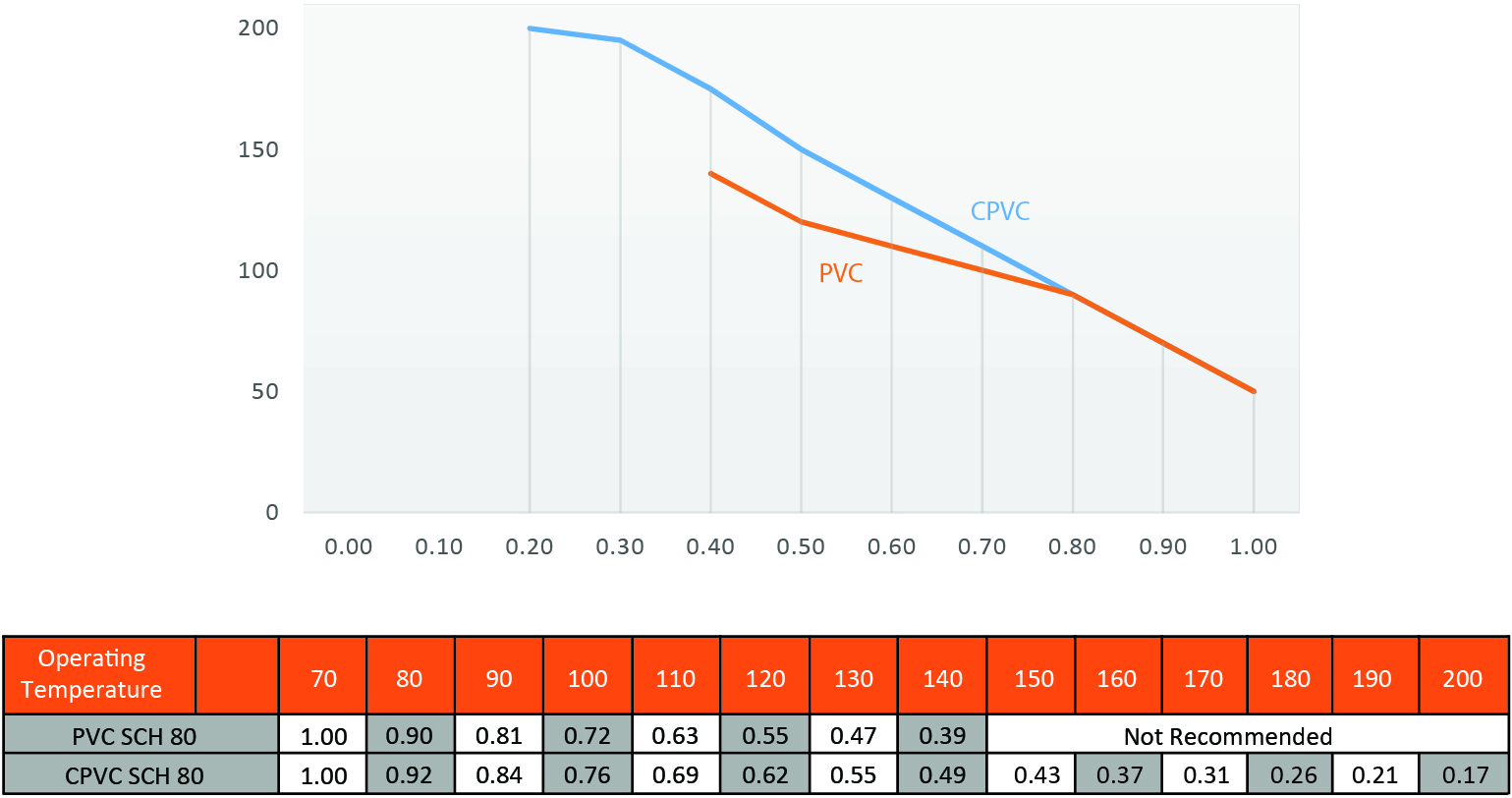
The maximum operating pressures listed on the right are based on the hydrostatic design of the product using water as a test medium at 73°F (23°C). The maximum operating pressure can be calculated from the following equations;
P = 20t/D-t
where;
P: Pressure
D: Average outside diameter
t: Minimum wall thickness
σ: Hydrostatic design stress (HDS)
2,000 psi (13.79 MPa) for PVC Type I, Grade 1
2,000 psi (13.79 MPa) for CPVC